Did multi-cultural societies become widely accepted in ancient history
Multicultural societies are today common and ubiquitous, but when did such societies become not only normal or typical but accepted or even celebrated ? Most likely, multi-cultural societies begin to evolve early in prehistory, as ethnic groups migrated to regions and integrated into existing societies. However, we rarely see multiculturalism celebrated until much later in historical periods when large states became the norm.
Contents
Early History
If we look at examples of early societies in Egypt, Mesopotamia, India, and China, we often see examples of migrations or contacts between different ethnic groups. [1] In many cases, these migrations or contacts are neutral or do not lead to any major confrontation. We do see cultures mixing their ideas in the form of introducing new gods to a region. Some cases where some level of multiculturalism may have been evident include societies that adopted foreign gods from their neighbors or other nearby cultures include the Hittites and Kassites, both Indo-Aryan speaking populations, who by around 1600 BC adopt gods from Anatolia and Mesopotamia. [2]
However, what is clear in many of these regions is that one main culture prevailed in any given period, as seen in artistic and intellectual expression. This does not mean cultures were suppressed. On the contrary, integration and assimilation were common, where local customs, languages, and social norms were generally adopted by the population merging into a given society. Interestingly, even if that minority culture took power, often they retained the previous prevailing culture or even went out of their way to emphasize that culture through revitalizing older traditions and languages. We see this in Kassite Babylonia in Mesopotamia, for instance, where the ruling population was Kassite and from Iran or India, while most of the native population presumably was from southern Mesopotamia. [3] This is likely unsurprising, as migrants presumably would have encountered a majority population and integrating into these majority populations meant that some level of assimilation was needed or at least to de-emphasize cultural expressions of a minority cultural group. In other words, societies may have been multicultural but multiculturalism was relatively limited, where expression of multiple cultures within one society was rare.
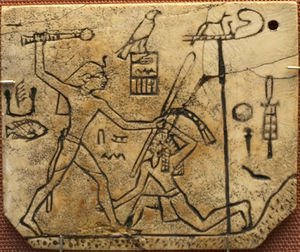
Nevertheless, many cases of denigrating or undermining populations do exist in the past. In particular, during times of conflict we see official art showing foreigners in a negative light or showing their inferiority to the ruling state (Figure 1). What this shows is that the level of multiculturalism expression were relatively limited and conflict often led to other cultures depicted in a demeaning way. [4]
Rise of Multiculturalism
By the rise of the Achaemenid Empire in Iran, in the 6th century BC, we see a new form of rule emerging. On the one hand, empires now began to expand much larger distances. In the case of the Achaemenids, their state reached from Egypt to Central Asia. With such a vast distance the new ruling dynasties needed new strategies to facilitate the maintenance of large states and enable populations within the large empire to accept their overlords. This may have led to the rise of multiculturalism, as we now begin to see more official celebration of different cultures within the Achaemenid state. For instance, in Mesopotamia, the Persian Achaemenid king depicted himself as Babylonian, while in Egypt we see depictions of the Achaemenid king as Pharaoh. The best example of this is from the reign of Darius I (522-486 BC; Figure 2). During the reign of Darius several representations of him as an Egyptian Pharaoh are depicted, including the rebuilding of important temples in Egypt.
Additionally, it was during the Achaemenid period from the 6th through 4th centuries BC that the world multiculturalism seems to have been first used in any language. In other words, societies were now officially recognized that they contained many cultural groups and that was seen as an asset rather than something that was deemphasized in official propaganda. An example of this, in fact, comes from Persepolis, where we see the architecture now incorporating styles from various areas of the empire (Figure 3). This is also the time we now begin to see the rise of large and multi-ethnic corporations and trade spanning distant regions, which suggests multiculturalism was found to have had not only ruling benefits, by keeping a large empire together, but facilitated trade and wealth. In fact, it is the increase of wealth and trade that may have created the incentive for multicultural empires to become popular not only in the ancient Near East but by the time the Roman Empire emerges in the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East. While the Romans did sometimes persecute faiths that they deemed threats, they also largely adopted a tolerant policy towards others cultures.
The rise of common languages during this time, first expressed in Aramaic, also likely explains how multiculturalism flourished. In effect, while cultural groups were free to worship as they please in most periods and conduct their own affairs, common language enabled the creation of an identity that groups could relate with to enable the state and, more significantly, the multicultural system to persist.
Given this rise of multiculturalism, it is perhaps not surprising that when we do get the rise of Christianity and Judaism, religions that were universal and monotheistic, they seem to have been accepted or tolerated in many areas of the Near East ruled by Iranian dynasties, such as the Parthians and Sassanians. These groups recognized, perhaps, the benefits of keeping a united state through the tolerance to different groups, even those that emphasized a narrower worldview of salvation that Rome found so threatening.
Continuity in Multiculturalism
In the Near East, and unlike Europe, multicultural empires persisted long after the fall of Rome and, in fact, continued until the fall of the Ottoman Empire in World War I. However, the rise of nationalism in the 19th century and creation of modern nation states did create the opportunity for new political identities that has, to some extent, led to the rise of some of the current conflicts in the Near East that appear to have some ethnic basis. What this shows is that more recent history does not necessarily reflect a historical pattern, where current conflicts between ethnic groups are more likely reflecting new power realities that did not translate to past societies in the region.
Summary
Multicultural societies have existed for millennia. However, how societies have adapted to multicultural realities has varied across time. In particular, the key shift we see in history is societies emphasizing one vs. multiple identities. We see this emphasis happening most profoundly starting during the Achaemenid period, with this pattern mostly continuing in the Near East long after the fall of particular states. In essence, populations saw the benefits of societies that were integrated while also maintaining their ethnic identities, where trade and economic benefits and linguistic commonality facilitated large, multicultural states.
References
- ↑ For information about historical migrations and multi-ethnic societies, see: Lucassen, Jan, Leo Lucassen, and Patrick Manning, eds. 2010. Migration History in World History: Multidisciplinary Approaches. Studies in Global Social History, v. 3. Leiden ; Boston: Brill.
- ↑ For information migrations and the adoption of local gods, see: Moret, Alexandre, and Georges Davy. 1970. From Tribe to Empire, Social Organization among Primitives and in the Ancient East. New York: Cooper Square, pg. 236.
- ↑ For information about how new, migrating cultures retained older cultures in given regions and the example of the Kassites, see: Ellerker, Sean. 2014. The Dawn of Civilization: 4,000-500 BC. Padstow: Matador, pg. 61.
- ↑ For information about how conflict led to intolerance in the past, see: Clarke, Steve, Russell Powell, and Julian Savulescu, eds. 2013. Religion, Intolerance, and Conflict: A Scientific and Conceptual Investigation. First edition. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Maltaweel, Admin and EricLambrecht